Dr. Ziyaur Rahman's Lab
Research Goals
The Rahman’s lab focuses on three areas:
- Ultra-long delivery system
- Abuse/Meth-Deterrent Formulations.
- 3D printing in Personalized Drug Delivery
Ultra-long Delivery System: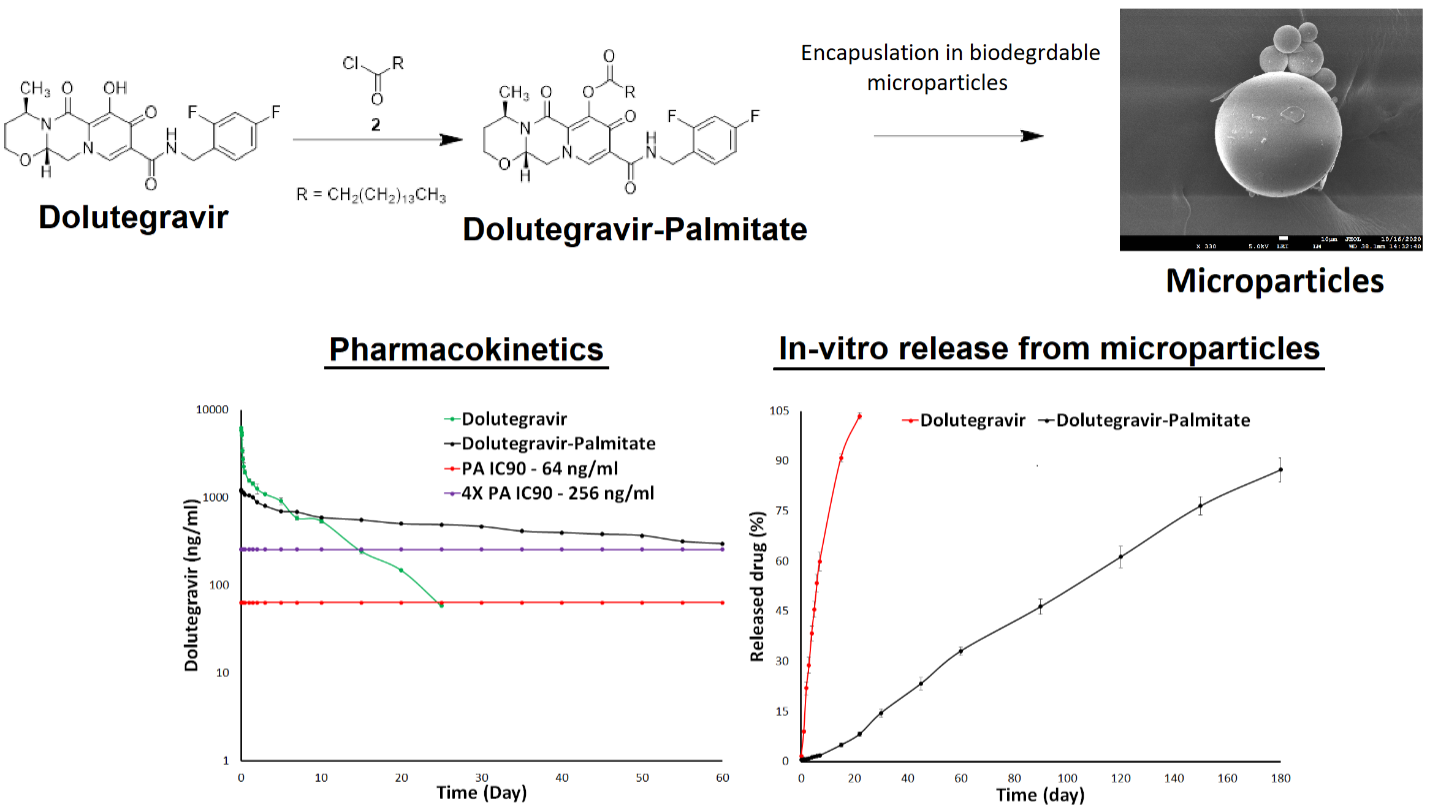
Since no eradication of HIV is currently possible, medications must be taken indefinitely to maintain virological suppression. This require development of long-acting formulations. The long-acting formulations may facilitate the maintenance of virologic suppression due to their long in-vivo half-life, thus requiring a limited number of administrations over a given period of time. The long-acting formulations of antiretroviral drugs will dramatically improve treatment adherence and clinical outcome as supported by data of long-acting formulations of antipsychotic drugs. Similar success story can be achieved for HIV treatment by the long-acting formulation of antiretroviral drugs. We are working to modify biopharmaceutical properties of FDA approved antiretroviral drugs and formulated into delivery system.
Abuse/Meth-Abuse Deterrent Formulations: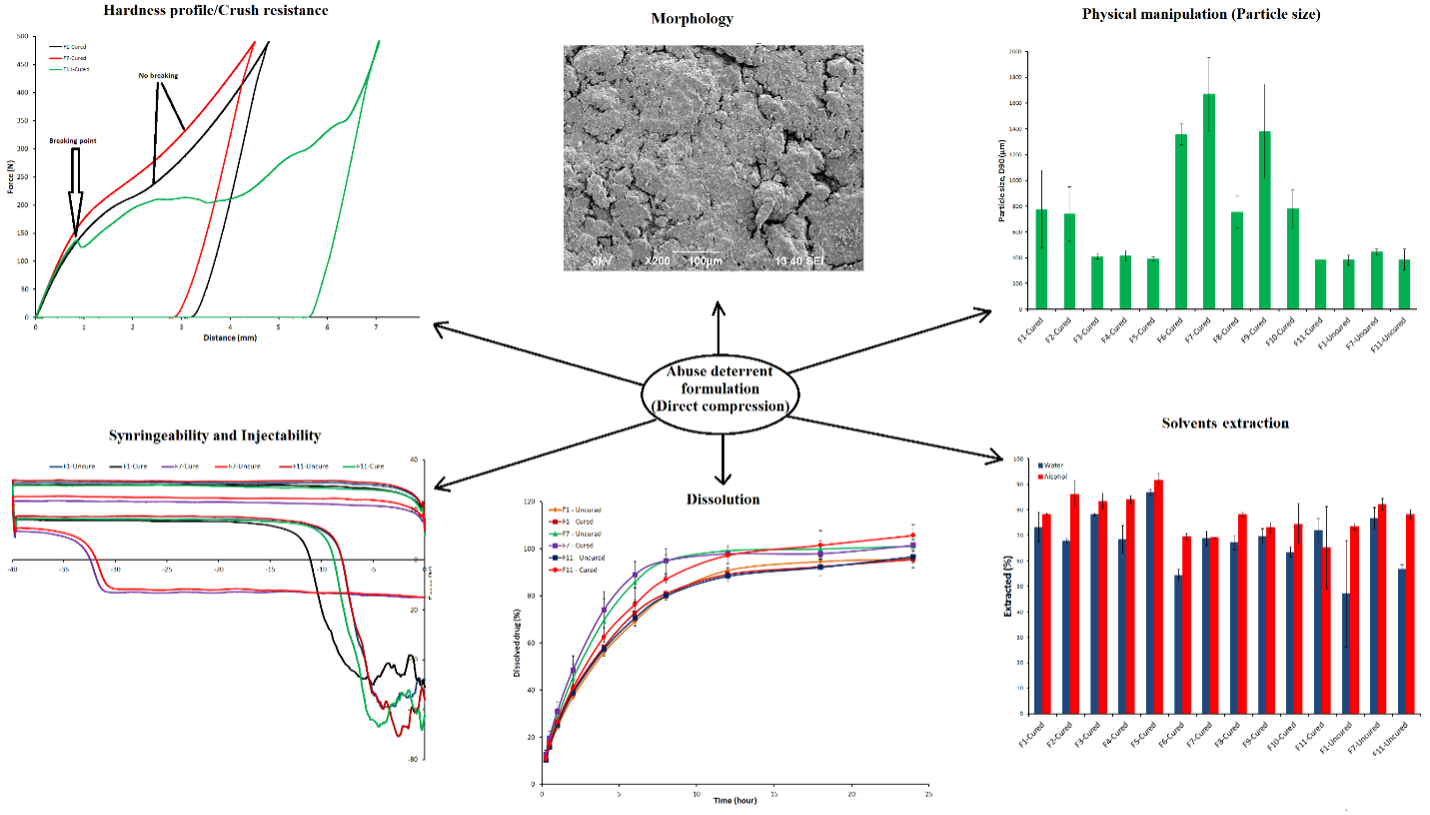
Abuse deterrent products (ADPs) or abuse deterrent formulations (ADFs) are highly specialized dosage forms designed to deter, do completely not eliminate the abuse of opioid products. Currently, we have two active grants on opioid abuse deterrent formulations from the Food and Drug Administration. We are assessing abuse potential of opioids and commercial products by route of smoking, and effects of excipient and stability conditions on opioids abuse by smoking. On the second grant, we are developing a non-abuse deterrent, chewable and bioequivalent to Hysingla formulation. Recently, we submitted another proposal to FDA on “In-Vitro Tools to Simulate Chewing of Pharmaceutical Opioid Drug Products” where we have proposed in-vitro chewing methods to predict human abuse potential of opioid products by route of chewing.
3D printing in Personalized Drug Delivery: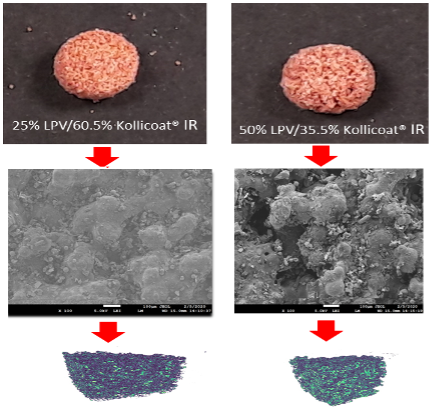
One of the methods of 3DP is selective laser sintering. The primary requirement of the SLS printer is laser sintering or melting of one or more of the components of the powder formulation, where the laser binds the powder particles together due to fusion/sintering. We have demonstrated feasibility of printing dose-flexible delivery system using this method. We are also exploring fused-deposition modelling and binder jetting methods for dose flexible delivery systems. Recently, we are awarded R56 grant from the NIH (Co-PI) for the development of dose flexible delivery system of anti-HIV drugs. Moreover, we are collaborating with industry (Dover Precision Components, Dr. Tanil Ozkan), as well as engineering faculty members, to address the need of the 3D printer for on-demand application that will meet GMP requirements. We have published research and review papers, and book chapters on 3DP in personalized medicines.
Lab Funding
- National Institutes of Health
- Food and Drug Administration
- Industry
- TAMU - T3, PCRP, PTTG
Recent Publications (out of 101, last two years):
Google scholar citation – 3,247h-index – 29
i10 index - 69
- Khuroo T, Dharani S, Mohamed EM, Immadi S, Wu Z, Khan MA, Lu D, Nehete P, Rahman Z (2021). Ultra-long Acting Prodrug of Dolutegravir and Delivery System - Physicochemical, Pharmacokinetic and Formulation Characterizations. International Journal of Pharmaceutics July 13;120889.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120889
-
Hamed R, Mohamed EM, Sediri K, Khan, MA, Rahman Z (2021). Development of stable amorphous solid dispersion and quantification of crystalline fraction of lopinavir by spectroscopic-chemometric methods. International Journal of Pharmaceutics June 1602:120657.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120657. -
Khuroo T, Mohamed EM, Dharani S, Afrooz H, Barakh Ali SF, Cook P, Khan MA, Rahman Z (2021). Coating characterization by hyperspectroscopy and predictive dissolution models of tablets coated with blend of cellulose acetate and cellulose acetate phthalate. AAPS PharmSciTech 22(3):122.
DOI: 10.1208/s12249-021-01986-z -
Charoo NA, Funkhouser C, Kuttolamadom MA, Rahman Z (2021). Opportunities and challenges of selective laser sintering 3D printing in personalized pharmaceutical manufacturing. American Pharmaceutical Review 24(2):60-64
-
Afoorz H, Rahman, Z, Daharni S, Khuroo T, Khuroo T, Mohamed EM, Nutan MTH, Reddy IK, Khan MA (2021). Preparation and characterization of dicarboxylic acids salt of aripiprazole with enhanced physicochemical properties. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology 26(4):455-463.
DOI: 10.1080/10837450.2021.1888978 -
Rahman Z, Dharani S, Khuroo T, Khan MA (2021). Potential application of USP paddle and basket dissolution methods in discriminating smokeless tobacco products. AAPS PharmSciTech 18;22(1):51.
DOI: 10.1208/s12249-020-01894-8. -
Afrooz H, Mohamed EM, Barakh Ali SF, Dharani S, Nutan MTH, Khan MA, Rahman Z (2021). Salt engineering of aripiprazole with polycarboxylic acids to improve physicochemical and taste properties. AAPS PharmSciTech 22(1):31. DOI: 10.1208/s12249-020-01875-x.
-
Hamed R, Mohamed EM, Rahman Z, Khan MA (2021). 3D-printing of lopinavir miniprintlets by selective laser sintering and quantification of crystalline fraction by XRPD-chemometric models. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 592:120059.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120059 -
Mohamed EM, Khuroo T, Afrooz H, Daharni S, Sediri K, CooK P, Arunagiri R, Khan MA, Rahman Z (2020). Development of multivariate predictive dissolution model of cellulose esters blend coated tablets. Pharmaceuticals 13(10):311.
DOI: 10.3390/ph13100311. -
Beg S, Almalki WH, Malik A, Farhan M, Aatif M, Rahman Z, Alruwaili NK, Alrobaian M, Tarique M, Rahman M (2020). 3D printing for drug delivery and biomedical applications. Drug Discovery Today 25(9):1668-1681.
DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.07.007 -
Dharani S, Barakh Ali SF, Afrooz H, Khan MA, Rahman Z (2020). Studying effect of glyceryl palmitostearate amount, manufacturing method and stability on polymorphic transformation and dissolution of rifaximin tablets. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 589:119785.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119785 -
Mohamed EM, Barakh Ali SF, Rahman Z, Ozkan T, Kuttolamadom MA, Khan MA (2020). Optimization of critical quality attributes of clindamycin palmitate hydrochloride printlets by response surface methodology. AAPS PharmSciTech. 21(6):232.
DOI: 10.1208/s12249-020-01775-0 -
Charoo NA, Barakh Ali SF, Mohamed EM, Kuttolamadom M, Ozkan T, Khan MA, Rahman Z (2020). Selective laser sintering 3D printing - An overview of the technology and pharmaceutical applications. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 46(6):869-877.
DOI: 10.1080/03639045.2020.1764027 -
Rahman Z, Dharani S, Barakh Ali SF, Nutan MTH, Khan MA (2020). Effects of diluents on physical and chemicals stability of phenytoin and phenytoin sodium. AAPS PharmSciTech 21(3):104.
DOI: 10.1208/s12249-020-1639-x -
Barakh Ali SF, Dharani S, Afrooz H, Mohamed EM, Cook P, Khan MA, Rahman Z (2020). Development of abuse-deterrent formulations using sucrose acetate isobutyrate. AAPS PharmSciTech 21(3):99.
DOI: 10.1208/s12249-020-01646-8. -
Harshita, Barkat MA, Das SS, Pottoo, FH, Beg S, Rahman, Z (2020). Lipid-Based nano system as intelligent carriers for versatile drug delivery applications. Current Pharmaceutical Design 26(11):1167-1180.
DOI: 10.2174/1381612826666200206094529. -
Dharani S, Barakh Ali SF, Afrooz H, Mohamed EM, Cook P, Khan MA, Rahman Z (2020). Development of methamphetamine abuse-deterrent formulations using sucrose acetate isobutyrate. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 109(3):1338-1346.
DOI: 10.1016/j.xphs.2019.12.003. -
Charoo NA, Rahman Z (2020). Integrating QbD tools for flexible scale-up batch size selection for solid dosage forms. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 109(3):1223-1230.
DOI: 10.1016/j.xphs.2019.12.007. - Rahman Z, Aqueel MS, Korang-Yeboah M, Zidan AS, Chen J, Alayoubi AY, Cruz CN, Ashraf M (2020). Evaluation of commercially available meth-deterrent pseudoephedrine hydrochloride International Journal of Pharmaceutics 575:118909.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118909
Google scholar
https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=BW3ahKUAAAAJ&hl=en
NCBI
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/myncbi/1Rel7PAiLOIQN/bibliography/public/
Research Awards
- ‘2020-2021 Mid-To-Senior Career Faculty Research Award’ Irma Lerma Rangel College of Pharmacy, Texas A&M Health Science Center, Texas A&M University
- ‘Regulatory Science Excellence’ award for ‘In vitro evaluation of meth deterrent formulation” by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, FDA, MD, USA, 2017.
- ‘Special Recognition’ award for ‘Outstanding research effort on Abuse Deterrent Formulations and for the first review of generic ADF through a pilot Review-Research team approach’ by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, FDA, MD, USA, 2016.
- ‘Team Excellence’ award for ‘Development of in-vitro quality metrics of acyclovir ointment and cream for the review of NDA # 20408 and Zovirax ANDAs’ by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, FDA, MD, USA, 2016.
- ‘FDA group recognition’ award for ‘Crystalline quantification in new tacrolimus extended release product for regulatory action’ by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, FDA, MD, USA, 2016.
- ‘Regulatory Science Excellence’ award for ‘Quantification of crystalline fraction of warfarin sodium in the drug products and in-use stability of commercial products’ by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, FDA, MD, USA, 2016.
- ‘Regulatory Science Excellence’ award for ‘Developing a performance matrix for equivalence evaluation of cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsions, paving the pathway for generic approval and provided scientific support to address sponsor’s CP request’ by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, FDA, MD, USA, 2015.
- ‘Team Excellence’ award for ‘Understanding the root cause of warfarin sodium product quality, development of discriminatory dissolution method and chemometric models for warfarin sodium fraction quantification’ by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, FDA, MD, USA, 2015.
- ‘Special Recognition’ award for ‘The outstanding first review of generic abuse-deterrent formulations through a pilot review-research team approach’ by Food and Drug Administration, MD, USA, 2015.
- ‘Certificate of Appreciation’ for serving distinguished CDER faculty 2014-2015, by Food and Drug Administration, MD, USA, 2015.
- ‘Team Excellence’ award for ‘The extraordinary contributions to the review and management of post approval changes to ANDAs’ by Food and Drug Administration, MD, USA, 2014.
- ‘Regulatory Science Excellence’ award for ‘Chemometric Methods for Tacrolimus Crystallinity Team’ for the quantification of crystallinity and discriminatory dissolution methods development for the tacrolimus products’ by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, MD, USA, 2014.
- ‘Team Excellence’ award for ‘Cyclosporine Ophthalmic Research’ by CDER, Food and Drug Administration, MD, USA, 2014.
Teaching Courses
- PHAR 642 Pharmaceutics I
- PHAR 641 Pharmaceutical Calculations
- PHSC 731 Process and Product Development
Lab Members
 |
 |
 |
|
Dr. Sathish Dharani |
Dr. Eman Mohamed |
Dr. Tahir Khuroo |